Learning designs as we've learnt,can be at the level of a subject, or subject components.
A learning design can be considered the framework which supports the learning experiences of a student.
A learning design comprises the following key elements:
Tasks that learners are required to do.
Resources that support learners to conduct the task.
Support mechanisms that exist from a teacher implementing it.

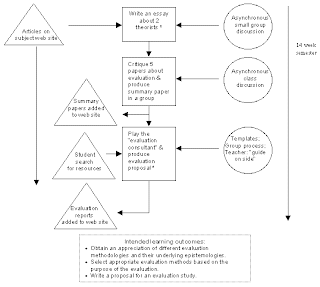
Representing learning activities: The learning activities are represented by a series of rectangles, arranged vertically. These activities represent the learner’s "journey". Each rectangle has a description of what the learners are required to do or produce. Activities that are assessable are distinguished with an asterisk (*).
Representing learning resources: Learning resources are represented by triangles to the left of the activity sequence. An arrow from a resource (triangle) to an activity (square) indicates that resources are available to the student when doing the activity. An arrow from an activity (square) to a resource (triangle) indicates that a resource is produced during the activity and becomes a resource for others to use later.
Representing learning supports: The learning supports are represented by circles to the right of the activity sequence. An arrow from a "circle" to a "square" indicates that support strategies are being used to assist the students in their learning.
Representing different combinations of activities, resources and supports: Resources and supports can be specific to an activity, they can be introduced before beginning an activity or when an activity is complete, or they may be available for the entire duration of the learning experience.
To represent this graphically, the following convention is suggested:
- If learning resources or supports are limited to particular activities, their availability is represented with a horizontal arrow to the specific activity for which they are available.
- If a learning resource or support is available for multiple activities then the resource triangle and/or support circle is drawn once (where it is firstly introduced to the students) and a vertical arrow indicates the resource and/or support is available for period of time.
- If students produce artefacts from a learning activity that are used as resources for subsequent activities, an arrow is drawn from the activity to the resource.
Below is an illustration of a learning setting in a classroom
As much as I agree that Learning designs can aid in providing a very effective visual as it clearly list the intended outcomes and the tasks and resources and support systems required to achieve our desired outcomes, it is incumbent that we be highly critical, analytical and meticulous when we try and produce one. Because of the rigid nature of a Learning design, once it has been finalised, it is difficult to make further changes to it.Moreover, it is expensive to produce.
In order to produce a foolproof learning design, the instructor has to go through all areas of planning and thinking thoroughly in his mind and this will undeniably take up a large amount of time and effort.However, if done successfully, the learning design can prove to be a very effective method for the planning of a wholesome learning experience and aid the instructor tremendously in achieving the desired outcomes.
I agree with you that learning designs requires one to be critical, meticulous and analytical bout it but don't you think it's hard to achieve this in reality? I mean if the instructors only revise their learning designs among themselves then it would not be very effective too... hmm. i guess like what we're doing in class, (reading about others' view on our learning designs) can improve and also REDUCE the amount of time and effort taken if one is to produce a learning design from the assessment of their own small group. =)
ReplyDeleteOne of the merit of learning design is that it is iterative; the designer can reorder the tasks in the first instance. Learning design authoring tools like LAMS and Exe allows one to make modifications to the learning design after trying out with the learners.
ReplyDelete